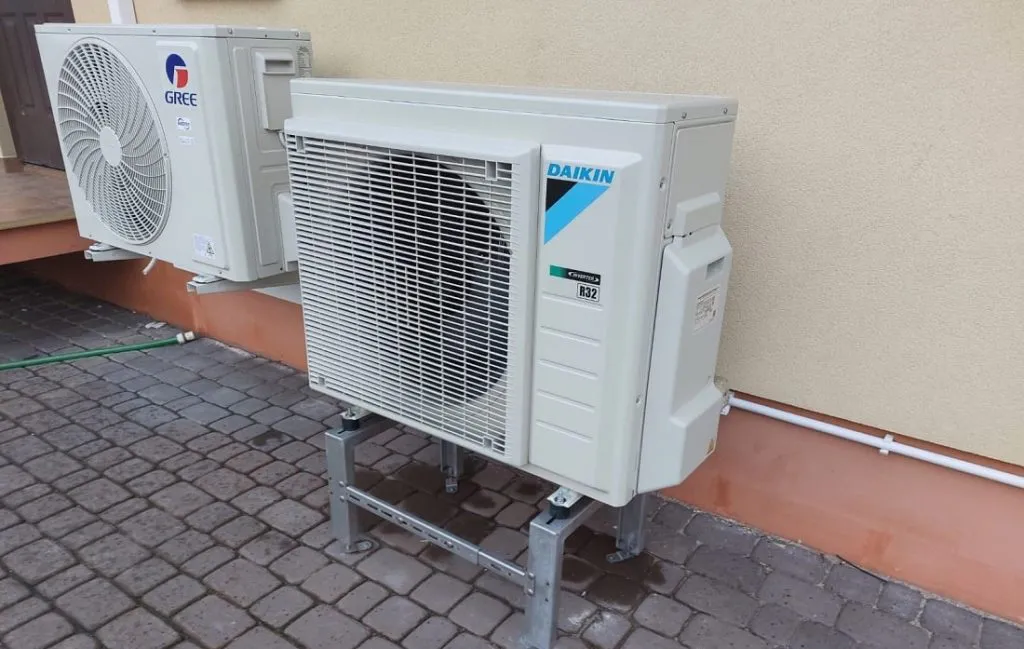

In the search for effective methods of heating or cooling a home, many of us face a difficult dilemma: should we choose an air conditioner or perhaps a heat pump? Both solutions provide indoor heating. It is worth noting that although an air conditioner can technically be classified as a type of air-to-air heat pump, there is a clear difference between a typical air conditioner and an air-to-water heat pump. So let’s take a closer look at these two solutions to understand them better. Let’s answer the question posed in the title – “Heat pump versus air conditioning: what are the differences?”.
The operating principle is based on the use of the refrigeration cycle, which involves several key stages:

Heat pumps use thermal energy extracted from an external, lower heat source such as ground, air or water. This process is carried out by means of a working fluid. For a heat pump to operate efficiently, three main components are required: the evaporator (outdoor unit), the condenser (indoor unit) and the appropriate refrigerant.
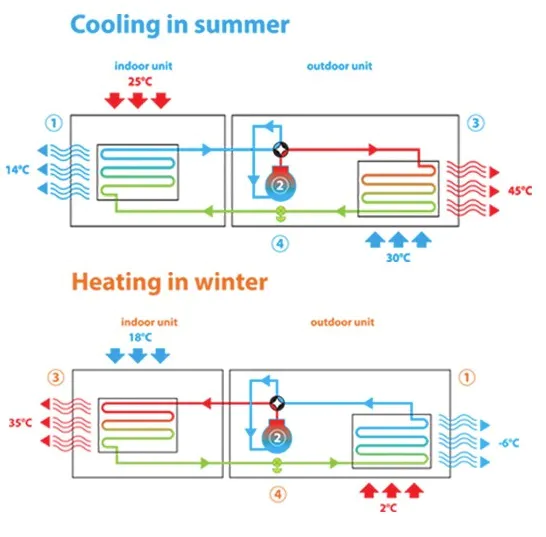
The basic idea of a heat pump is to exploit the properties of the refrigerant, which circulates in a closed circuit between two heat exchangers: an evaporator and a condenser.
In order to use a heat pump to cool a house, this process must be reversed, meaning that heat is removed from the inside of the building and discharged to the outside, resulting in a lower temperature inside.
Let us now turn to the advantages of both solutions. Air conditioning offers a number of benefits for users, among which it is worth highlighting:
Benefits of having a heat pump to consider when choosing a heating and cooling system:
When considering the advantages of both solutions, the individual needs and conditions of the building must be taken into account in order to select the system that best meets the users’ expectations and ensures thermal comfort for many years to come.

What are the differences between a heat pump and air conditioning? Let’s start with an analysis of energy efficiency. Air-to-water heat pumps efficiently use ambient energy to both heat and cool rooms, resulting in significant savings in electricity costs. Importantly, they maintain high efficiency even at lower temperatures, reaching as low as -25°C, although it is worth noting that their efficiency may decrease slightly in the case of extremely low winter temperatures.
In contrast, air conditioners are more efficient at cooling, but their performance in heating mode is slightly lower. They perform admirably during the hot months, but in winter their heating capacity can be limited, leading to increased electricity consumption and, ultimately, higher electricity bills. This is a factor worth considering, especially when planning to use air conditioning as the main heating source in the home. Air conditioners with a heating function can be effective in moderate climatic conditions, but it should be remembered that their heating efficiency has its limitations. Most of these units operate efficiently up to a temperature of around -10°C. When the temperature drops below this, air conditioners can struggle to provide sufficient heat. This can result in the need for additional heating sources during the harsh winter months.
In terms of cost, installing air conditioners is usually cheaper than installing heat pumps. Upfront costs for air conditioners are lower and installation is simpler, making them an attractive choice for those on a tight budget. On the other hand, despite higher installation costs, heat pumps can save money in the long term due to their higher energy efficiency, leading to lower electricity bills.
Choosing between an air conditioner and an air-to-water heat pump is a decision that requires consideration of many factors. Both air conditioners and heat pumps have their own unique benefits and applications that can suit different user needs. Air conditioners offer effective cooling on hot days, improved air quality, humidity control and relatively simple installation, making them an attractive option for those looking for a quick and easy way to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Air-to-water heat pumps, on the other hand, stand out for their higher energy efficiency, versatility of operation, long life and low CO2 emissions, making them an ideal solution for those looking for a more advanced and environmentally friendly heating and cooling system. Before making a final choice, it is advisable to carefully analyse individual needs, building conditions and available budgets in order to select the solution that best meets users’ expectations and ensures thermal comfort for many years to come.
Sources:
https://evolive.pl/uslugi/pompy-ciepla/
https://www.daikin.pl/pl_pl/Porady-Daikin/pompy-ciepla-a-klimatyzatory.html
https://www.daikin.pl/pl_pl/grupy-produktow/klimatyzacja/ururu-sarara.html
https://budotom.pl/pompa-ciepla-powietrze-powietrze-a-klimatyzacja/
https://www.aleklima.pl/artykuly/jak-dziala-klimatyzacja;more=2113611023
ul. marsz. Józefa Piłsudskiego 74/320
50-020 Wrocław, Polska
NIP: 8971903418
Jesteśmy na terenie całej Polski!
2026 © evolive.pl
Logowanie
Rejestracja