
In an era of rapid technological development and growing environmental awareness, more and more people are considering alternative energy sources. Of particular interest in this category is the issue of backyard wind turbines, which are not only a fascinating innovation but also a practical solution for households. The winds permeating our surroundings, which were once merely seen as a force of nature, are now becoming a potential source of electricity. Let us therefore consider the solutions, considerations and challenges of how wind can become our ally in providing clean and sustainable electricity. In this article, we will also answer the question posed in the title: what works better: a domestic wind turbine – vertical or horizontal?
Choosing between a vertical and horizontal wind turbine is a key step when designing a home wind turbine.
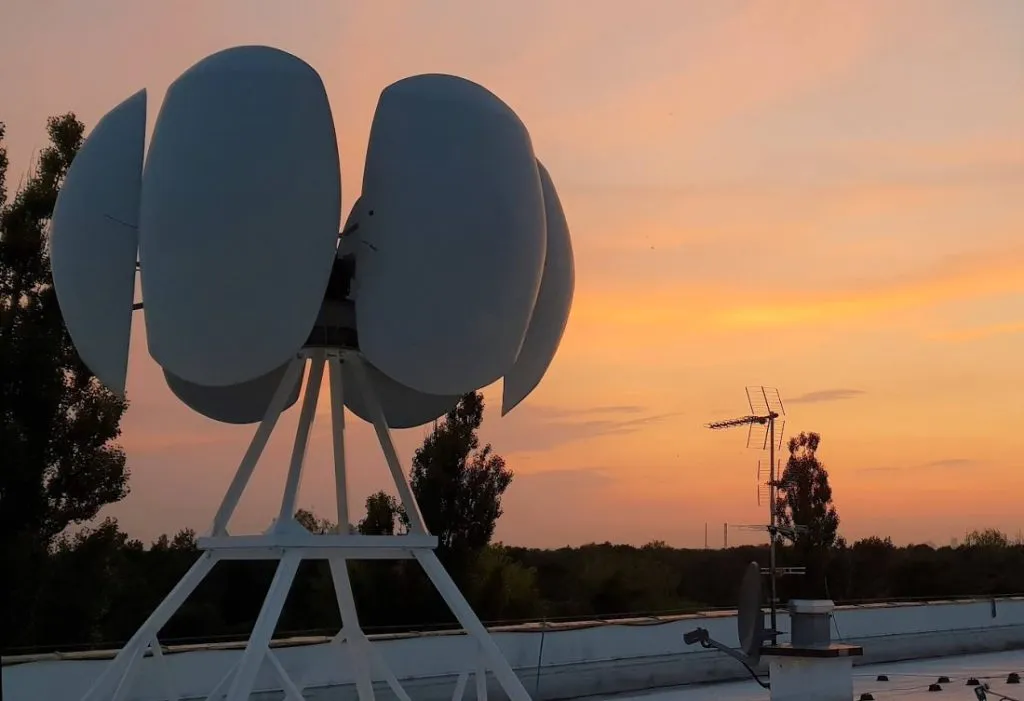
Vertical home wind turbines, such as the Ecorote models, adapt better to changing wind directions. Their design allows them to generate energy efficiently without having to adapt to one fixed direction. In variable wind conditions, they are more versatile and efficient, making them attractive for areas with unstable wind conditions. The rotor diameter of vertical turbines tends to be smaller than their horizontal counterparts, making them more compact and better suited to confined spaces. This also translates into lower noise emissions compared to horizontal turbines, which is important for environmental protection and occupant comfort. Nevertheless, vertical turbines have some disadvantages. Under conditions of constant wind direction, they can show potentially lower efficiency than their horizontal turbines.
Domestic horizontal wind turb ines can achieve higher efficiencies under conditions of constant wind direction. They are particularly effective when the wind is blowing from one direction. Horizontal turbines typically have larger rotors, which affects their ability to extract energy from stronger winds. In contrast, their efficiency can decrease when the wind direction is variable, so they can compare negatively with vertical turbines. In addition, due to the higher load on the blades, they generate more noise emissions, which is a significant environmental and social aspect.

A domestic wind turbine with a vertical axis of rotation ECOROTE!
The Ecorote wind turbine is characterised by:
Calculating the predicted energy production of a home wind turbine using the average wind speed is a key step in assessing the efficiency of a given system. For this task, it is useful to use appropriate formulas that take into account the technical parameters of the turbine and the weather conditions. A formula that is often used for this purpose is one that is strongly related to rotor efficiency.
The formula for turbine power output:
Where:
P – output power
ρ – air density
A – cross-sectional area of the wind stream calculated using the formula A=(π*D2)/4, where D – diameter of the circle swept by the rotor blades, i.e. the sum of the lengths of the two blades
ηm – mechanical efficiency
ηel – efficiency of the generator
Cp – wind power factor
Example calculation:
Suppose we have a wind turbine with a blade area of 10m2. The coefficient Cp = 0.593. The average annual wind speed in Poland is 7 m/s and the air density is 1.225 kg/m3. Mechanical efficiency ηm = 95%, generator efficiency ηel = 90%.
Based on the formula:
The P-value obtained from the calculation will represent the theoretical power output of the turbine for a given time and atmospheric conditions. When analysing the energy production of a domestic wind turbine over time, the varying wind speeds and efficiency of the turbine under different conditions should be taken into account.
Since the beginning of 2023, a number of regulatory changes have been introduced that affect the installation of domestic wind turbines. Domestic wind turbines between 3 and 12 metres in height with a maximum capacity of 50 kW have been exempted from the requirement to obtain planning permission. However, it is worth noting that there are other formalities that must also be fulfilled in this situation:
Analysis of the wind speed in a given region is a key part of wind turbine design. Wind speed has a direct impact on the output of the turbine. Locating a wind turbine on a building that is above ambient level will usually yield the greatest benefit. Therefore, it is important to use expert knowledge and get support from an experienced installer when assessing the viability of a project.
Theheight of a wind turbine mast is a key factor in determining its efficiency. While lower masts may be more accessible, they also limit the potential wind speed at which the rotor can operate. For vertical turbines, lower masts can be advantageous due to their compact design. For horizontal turbines, on the other hand, higher masts will be better to achieve more stable wind conditions.
Buying a domestic vertical/horizontal wind turbine on your own carries certain risks, especially for those unfamiliar with the specifics of the industry. One of the main risks is the possibility of buying a turbine whose technical specifications do not meet the actual needs of the user.
Purchasing a windmill with the wrong capacity in relation to the wind conditions in a given location can result in an inefficient use of wind potential. It is necessary to understand how to correctly estimate the power and capacity of a windmill, which is crucial for optimal plant operation (see section 2).
There is a risk of unfair commercial practices in the market, such as false declarations of the technical performance of a wind turbine. Many dishonest sellers may present less efficient windmills as more efficient, leading to the purchase of a unit that does not meet expectations.
How do you protect yourself from these risks?
With the rapid development of technology and growing environmental awareness, more and more people are starting to consider alternative energy sources. Household wind turbines stand out as an interesting innovation, offering practical solutions for households. The choice between a vertical or horizontal turbine depends on individual needs and local conditions. Regardless, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the technical parameters, local regulations and the risks involved in buying on the wind turbine market.
Sources:
ul. marsz. Józefa Piłsudskiego 74/320
50-020 Wrocław, Polska
NIP: 8971903418
Jesteśmy na terenie całej Polski!
2026 © evolive.pl
Logowanie
Rejestracja